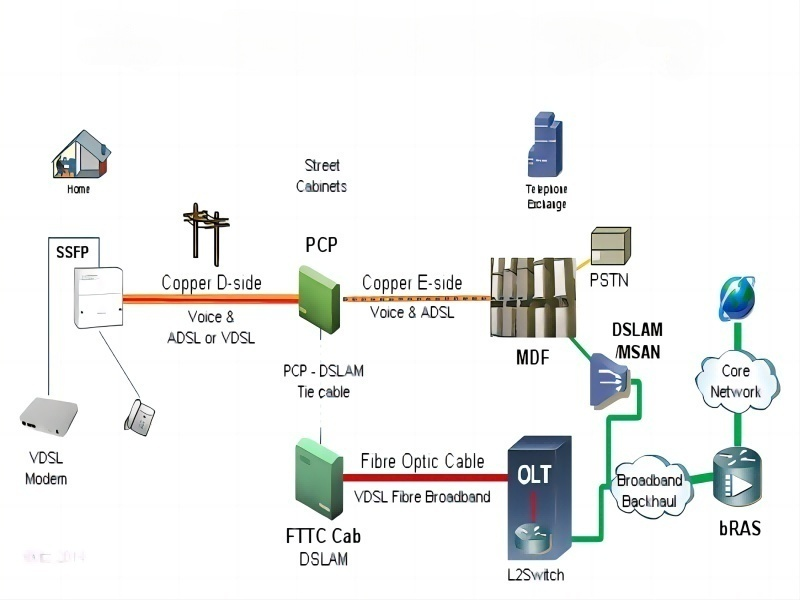
Data Center, abbreviated IDC, is the Internet Data Center. The reason why it is not called “DC” directly is mainly to avoid confusion with direct current (Direct Current).

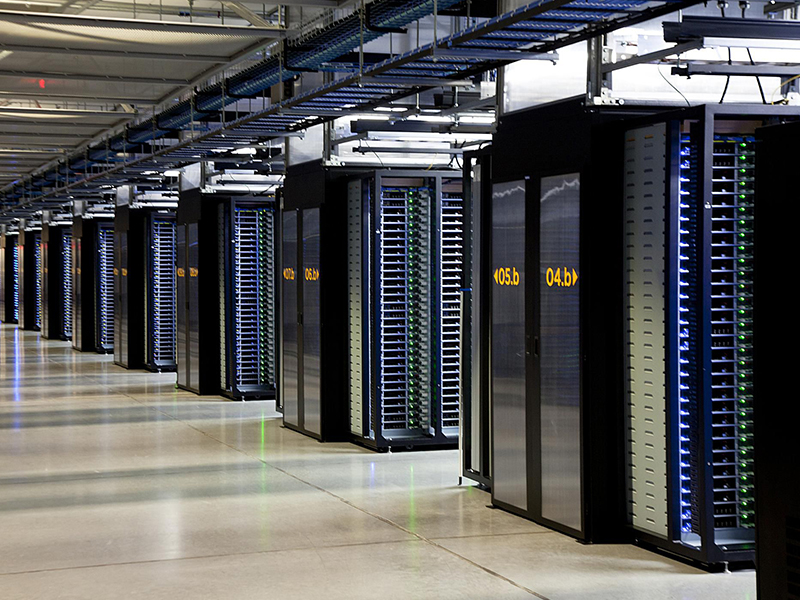
From a functional point of view, the data center is an oversized computer room with many servers dedicated to centralized data management (storage, calculation, and exchange). Data centers are important infrastructure such as water and power plants. They are the driving force behind the digital economy and the support base for national and social development.
Data center development stages
In the 1960s, humanity was still in the mainframe era. At that time, in order to store computer systems, storage systems and power equipment, people built computer rooms and called them server farms, which are considered the earliest prototypes of data centers.
In the 1990s, with the birth and vigorous development of the Internet, many companies began to implement informatization. They built their own websites and also built a large number of email, FTP, OA office automation and other servers.
Some companies place servers in internal computer rooms. There are also some companies that don’t have many servers but are unwilling to put them in offices (noisy, prone to power outages, and low security), so they “host” them in the operator’s computer room and rent the operator’s space, electricity, and network bandwidth. Let the other party manage and maintain it on your behalf.
In 1996, Exodus, an American company specializing in the construction of computer room facilities and bandwidth service names, first proposed the name “IDC”. The concept of a data center began to take shape. This is the first phase of IDC’s data center development.
In 1997, Apple introduced a virtual machine called a “Virtual PC.” Later, VMWare also launched the now-famous VMWare Workstation, marking the arrival of the virtual machine era and laying the foundation for the evolution of data centers.
As time went on, the first generation of data center hosting services began to become more refined, extending from full server hosting to website hosting and virtual hosting services. In other words, on a certain server, through virtual host software, N website hosts are virtualized and rented to N customers.
In addition to websites, diversified services such as data storage rental have also emerged. This is the second phase of IDC data center.
At the beginning of the 21st century, companies such as Amazon and Google proposed cloud computing, thus bringing the data center into the third stage (cloud computing stage), which continues to this day. Cloud computing is the second stage of upgrade and evolution. It uses virtualization technology and container technology to fully realize the pooling of data center server computing resources. All CPU, memory, hard disk, and other resources are managed by more powerful virtualization software and then allocated to users.
It has evolved from physical hardware leasing to virtual hardware leasing, and even software platform leasing and service leasing. IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, just show up in front of us.
Data center structure
In terms of hardware type, the data center is similar to the internal computer room of the enterprise that we often see before, but the specifications, grade and management level are higher.

Overall, data center hardware is divided into two categories, namely main equipment and supporting equipment. The main device is the device that truly realizes computing and communication functions, that is, IT computing equipment represented by servers and storage, and communication equipment represented by switches, routers, and firewalls.
Support equipment refers to the underlying basic support equipment ( including some facilities) that exists to ensure the normal operation of the main equipment.
The basic basic supporting equipment and facilities are divided into many types, mainly power supply and distribution systems and heat dissipation and refrigeration systems, as well as fire protection systems, monitoring systems, building management systems, etc.
Master device
The most basic equipment in the data center is, of course, the server. A server is actually a high-performance computer. Everyone should have seen it. It is the same as a desktop computer, including CPU, memory, motherboard, hard disk, graphics card (GPU), power supply, etc.
In the past, servers were basically based on Intel architecture (earlier, there were PowerPC, SPARC, etc.). Nowadays, with the changes in national policies, domestic CPUs have risen and occupied an increasing share. These domestic CPUs use ARM architecture, which is more cost-effective and lower cost.
A standard rack is usually 42U in height. U is a unit that represents the external dimensions of the server and is the abbreviation of unit. 1U is equal to 4.445cm. The width of the rack is generally 600mm or 800mm.
There are many types of rack depths, including 600mm, 800mm, 900mm, 1000mm, 1200mm, etc. In general, IT equipment (server) racks are deeper (1100mm or 1200mm), while communication equipment racks are shallower (600mm).
In addition to servers, the IT equipment in the rack also includes professional storage devices such as disk arrays. Currently, mainstream computer storage hard drives are divided into two types: HDD and SSD. HDD is our traditional mechanical hard drive, while SSD is a solid-state drive that is gradually becoming more popular. SSD is a semiconductor memory with fast storage speed and small size, so it is very popular. However, it is expensive. For data centers, HDD is still the mainstream choice due to cost-effectiveness considerations. SSDs are currently mainly used for high-end customers and businesses that require high performance.
In addition to IT computing equipment, there is also data communication equipment such as switches, routers, and firewalls.
TOR switch is a common term in the data center field. As the name suggests, it means the switch at the top of the rack. This type of switch is the lowest network switching device in the data center. It is responsible for connecting the servers inside the rack and connecting to the upper level switches.
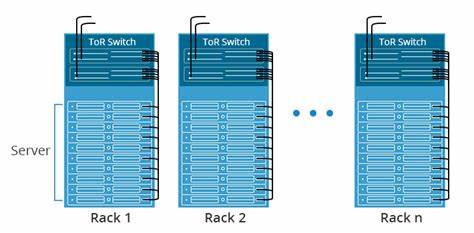
In fact, the rack switch does not say that it must be placed on the top of the rack. It can be at the top of the rack, or in the middle or bottom of the rack. It is usually placed at the top simply because it is most conducive to internal wiring.
Further up the rack, there are a row of racks and N rows of racks. To connect these racks and servers, data center networking technology is required.
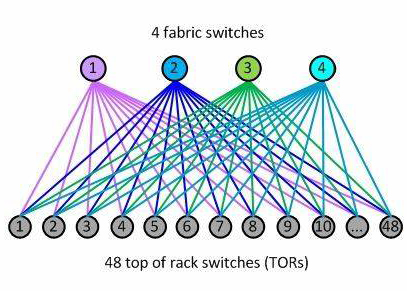
The most popular data center networking architecture today is Spine-Leaf.
It is worth mentioning that in order to transmit data with high bandwidth, data centers now generally use optical fiber instead of network cables. Therefore, optical fibers, optical modules and optical communication equipment (OTN, etc.) have become important components of the data center.
Especially for optical modules, high-speed optical modules (such as 400G) are very expensive and account for a large part of the cost of the data center, which restricts development.

There is also a popular optical communication term called DCI, which is Data Center Inter-connect. Nowadays, distributed deployment is popular, and the data traffic between data centers is very large, which requires high bandwidth. Operators and cloud service providers develop DCI and build specialized optical communication backbone networks between data centers, which is a large market.

Data center equipment and facilities
- Power supply and distribution
Power supply is the basis for the normal operation of the data center. Without electricity, data centers are scrap metal.
The main function of the power distribution equipment in the data center is to switch on and off, control and protect electric energy. The most important power distribution equipment is the power distribution cabinet.
Data center power distribution cabinets are divided into medium voltage power distribution cabinets and low voltage power distribution cabinets. The medium voltage distribution cabinet is mainly of 10kV voltage level. It is connected to the upstream mains power supply and the downstream low voltage distribution cabinet. Low voltage distribution cabinets are mainly 400V voltage level, which further converts, distributes, controls, protects and monitors electrical energy.
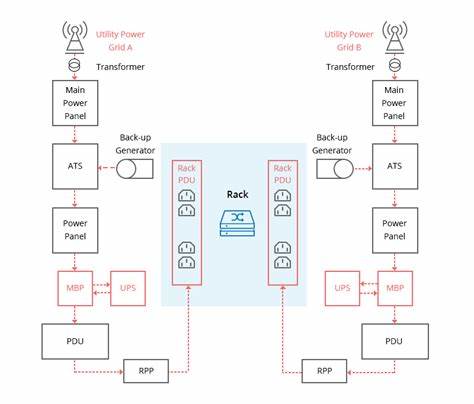
In addition to power distribution cabinets, in order to ensure normal power supply in emergencies, data centers are also equipped with a large number of UPS (uninterruptible power supplies) and even diesel generator sets.
“UPS+mains power” is a traditional power supply solution. Nowadays, the most popular solution is the “HVDC+mains power” solution.
HVDC is high voltage direct current, high voltage direct current transmission. The difference between it and UPS involves a more complex knowledge of strong electricity. In short, “HVDC+mains power” is more reliable and safer, and the power supply efficiency is stronger than “UPS+mains power”. It is the mainstream development trend of uninterruptible power supplies.
Let’s talk briefly – 48V and 220V.
IT equipment such as servers typically use 220V AC, while core network, wireless, and other communications equipment mostly use -48V DC.
The main power supply is usually AC. Data centers generally provide both -48V DC and 220V AC (through AC-DC conversion and DC-AC inverter conversion).
In fact, DC is now becoming the choice of more data centers (such as Google) because DC has smaller losses and higher power utilization, which is in line with the current trend of high energy consumption in data centers with high computing power.
- Heat dissipation and refrigeration
The refrigeration system is the second largest energy consumer in the data center after the main equipment. At present, data center cooling mainly includes two methods, one is air cooling and the other is liquid cooling.
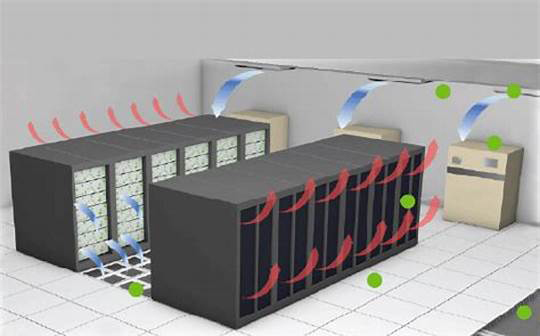
Air cooling generally uses air-cooled air conditioning systems. Like our home air conditioners, data center air-cooled air conditioners are also divided into indoor units and outdoor units. Relatively speaking, the technology is mature, the structure is simple, and it is easy to maintain.
Liquid cooling uses liquid as a refrigerant to cool and dissipate heat.
The thermal conductivity of liquid is 25 times that of air. At the same volume, the heat carried by liquid is nearly 3,000 times that of air. From a noise point of view, at the same heat dissipation level, the noise of liquid cooling is 20-35 decibels lower than that of air cooling. From the point of view of energy consumption, liquid cooling saves 30%-50% of electricity compared to air cooling.
At present, liquid cooling technology is generally optimistic about the industry, but it is still in the exploratory stage. Overall, the market prospects for liquid cooling are very broad, and the market size is said to exceed 100 billion.
Regarding cooling and heat dissipation, it is worth mentioning that near-end cooling methods such as cabinet pool level, row level and cabinet level are emerging and becoming the mainstream choice for new data centers.
Traditional refrigeration is at room level, where the entire computer room is air-conditioned and refrigerated. This method has a very long cooling path and is too inefficient. It cannot meet the cooling needs of high-power equipment and consumes a lot of energy.
Cabinet pool level, row level and cabinet level are based on a cabinet pool, row of cabinets or a single cabinet as the center for heat dissipation design.

For row-level cabinet heat dissipation, air ducts are designed based on a row of cabinets. In this way, the airflow path is significantly shortened and the heat dissipation efficiency is very high.
In addition to power distribution, heat dissipation and refrigeration, the data center also has some equipment and facilities related to management and operation and maintenance, such as dynamic environment monitoring systems, building automatic control systems, fire protection systems, etc. Dynamic environment monitoring refers to power and environment monitoring, which monitors and manages the operating status of the data center in real time.
Based on the traditional dynamic environment monitoring system, DCIM began to evolve. DCIM’s full name is Data Center Infrastructure Management, which was proposed by Garter, a well-known consulting company. Its management scope is more comprehensive, using tools to monitor, manage and control all the IT equipment and supporting infrastructure in the data center.

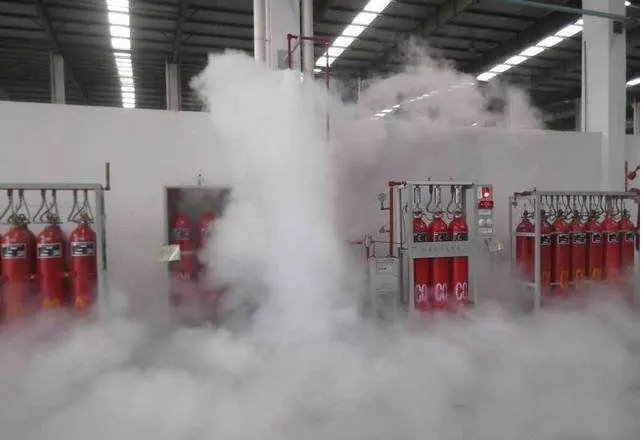
The fire protection system in the data center is quite interesting. Because the computer room is full of electronic equipment, if a fire occurs, you must not spray water, foam or dust directly. Then what do we do? Gas fire extinguishes.
After a fire occurs, the fire alarm and smoke sensor sound, and then the computer room area can release inert gases such as argon and nitrogen to deprive the flame of oxygen and extinguish the fire (it can be done in about tens of seconds).

Modular data center
The data center is a huge system, the construction process is very complex and cumbersome, and the construction period is also very long. In recent years, in order to deploy data centers more quickly and flexibly, manufacturers have introduced the concept of modular data centers. It is to integrate the structural system, power supply and distribution system, HVAC system, fire protection system, lighting system, integrated wiring, etc. of the data center into “building blocks” one by one. Then, after transporting the “building blocks” to the site, they can simply be hoisted and set up to complete construction and deployment.
Using this method, the construction cycle of large data centers is reduced from 18-24 months to about 6 months, and the economic benefits are obvious.

The data center is an important information infrastructure in the digital era and an important carrier of computing power, which directly determines the country’s digital competitiveness.
In addition to the surge in numbers, data centers are developing in a green and intelligent direction, actively introducing AI to improve energy efficiency and reduce operational complexity.
Let’s wait and see if there will be any new data center changes in the future!